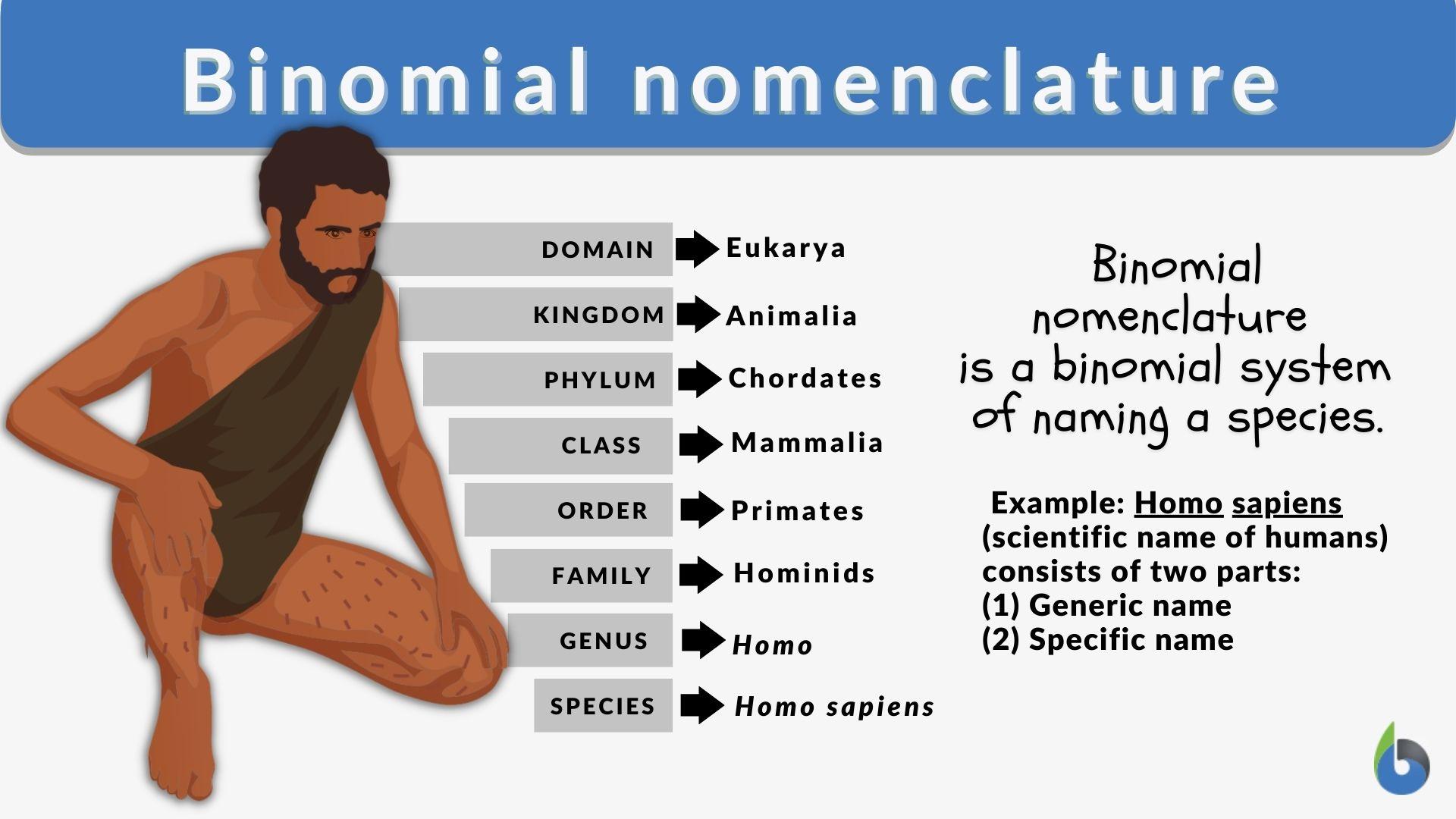
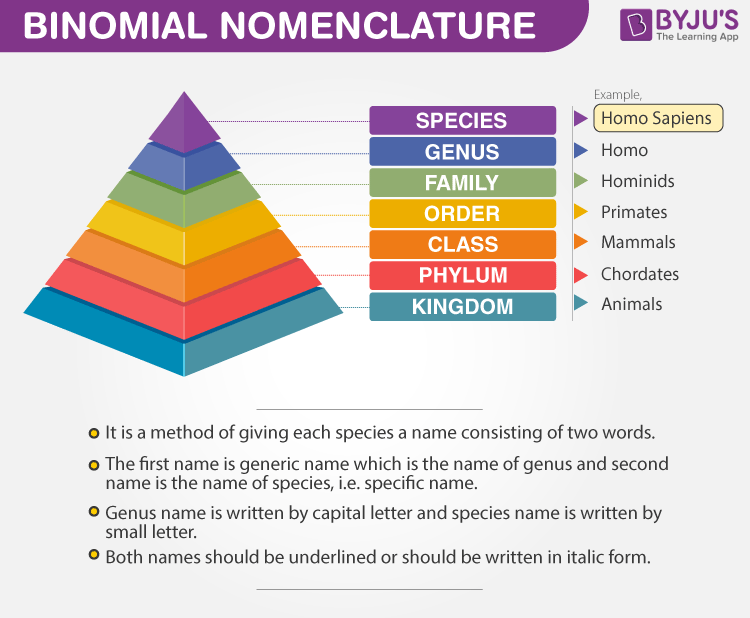
Binomial nomenclature, also known as binary nomenclature, is a formal naming system used in taxonomy to assign unique scientific names to living organisms. Each species is given a name consisting of two parts – the genus and the specific epithet.
This system, established by Carl Linnaeus, ensures clear and accurate identification of species across different languages. For example, the ladybug Harmonia axyridis follows this naming convention. Understanding binomial nomenclature is crucial for scientists and researchers in accurately categorizing and communicating about the vast diversity of life on Earth. Through these unique scientific names, scientists can precisely refer to individual species and avoid confusion in scientific communication.
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature, also known as binary nomenclature, is a formal method used to name species by assigning a name consisting of two parts in Latin grammatical form.
Binomial nomenclature assigns a two-part scientific name to each species. For instance, the ladybug in the U.S. is called Harmonia axyridis. The first part, like Harmonia, represents the genus.
Binomial Nomenclature is a formal naming system for species using two-word Latin names. Let’s explore the essential rules governing this system:
Binomial nomenclature, commonly known as the naming process in taxonomy, assigns a two-part scientific name to each species. This system utilizes Latin grammatical forms and words from other languages, with the first part designating the genus and the second representing the specific epithet.
It is the universally accepted way to classify and identify living organisms.
In the naming process of binomial nomenclature, scientific names are composed of two parts: the genus and the specific epithet. The genus represents a broader group or category to which the species belongs. It is always capitalized and written first in the scientific name.
The specific epithet is the second part of the scientific name. It provides a unique identifier for the species within the genus. The specific epithet is not capitalized and follows the genus name.
Binomial nomenclature provides a standardized naming system for living organisms. Here are a few examples of scientific names:
| Example | Scientific Name |
|---|---|
| Lion | Panthera leo |
| Blue whale | Balaenoptera musculus |
| Apple tree | Malus domestica |
These scientific names clearly demonstrate the use of the genus and specific epithet in binomial nomenclature.
Binomial nomenclature, also known as binary nomenclature, serves as the fundamental system for scientifically naming living species. This method involves assigning a two-part Latin-based name to each species. The first part represents the genus, while the second denotes the specific epithet. This strong foundation established by binomial nomenclature helps in the systematic categorization and identification of diverse organisms.
The use of binomial nomenclature in taxonomy facilitates the efficient classification of species. By employing distinct scientific names, this system aids scientists in organizing the myriad of species found within the biological realm into coherent groups. Each organism is accurately positioned within the taxonomic hierarchy, ensuring a well-structured and precise categorization.
Implementing binomial nomenclature in practice involves adherence to specific rules. The first component denotes the genus, which always begins with a capital letter. On the other hand, the specific epithet follows the genus and is not capitalized. Both components are italicized, emphasizing their scientific nature. Furthermore, this nomenclature system offers a standardized approach for naming living organisms, fostering global consistency and clarity within the scientific community.
Carl Linnaeus, a renowned Swedish botanist, physician, and zoologist, is widely acknowledged for his substantial contributions to the establishment of binomial nomenclature, which is the formal system used for naming species of living things. Linnaeus’ innovative approach revolutionized the classification and naming of organisms, providing a standardized method that is still widely utilized in biological sciences today.
Carl Linnaeus is often revered as the Father of Binomial Nomenclature due to his pivotal role in developing and popularizing this systematic nomenclature method. Linnaeus recognized the need for a more organized and universally accepted system for naming and classifying organisms, which led to his groundbreaking work in the field of taxonomy.
Linnaeus’ taxonomy system, known as binomial nomenclature, introduced the use of a two-part naming system to denote species, consisting of the genus and the specific epithet. This systematic approach facilitated clearer communication and categorization of biological diversity, simplifying the process of identifying and referencing various organisms.

Binomial nomenclature, also known as binary nomenclature, serves as a formal system for naming species of living organisms by giving each a unique name composed of two parts. This system was first established by the renowned biologist Carl Linnaeus and is still widely used today. The importance of binomial nomenclature lies in its uniqueness and standardization, as well as its role in facilitating identification and communication within the scientific community.
The first aspect that makes binomial nomenclature essential is its ability to provide a unique identifier for each species. By assigning a two-part scientific name to organisms, such as Harmonia axyridis for the ladybug, binomial nomenclature ensures that no two species share the same name.
Moreover, binomial nomenclature brings standardization to the naming process. All scientists universally recognize and follow this nomenclature system, eliminating any confusion that could arise from multiple names for the same species. This consistency promotes clarity and accuracy in scientific literature and communication, enabling researchers to build upon existing knowledge effectively.
Binomial nomenclature simplifies the identification and classification of species. With the use of specific epithets, the second part of the scientific name, scientists can categorize organisms into groups based on common characteristics or traits. This classification system enhances our understanding of the diverse range of species in our ecosystem.
Furthermore, binomial nomenclature facilitates seamless communication between researchers around the globe. Scientists from different countries and languages can communicate effectively using the standardized Latin-based scientific names, ensuring a clear and accurate exchange of information. This international language of taxonomy is crucial for collaborations, research papers, and the overall advancement of scientific knowledge.
Binomial Nomenclature has a rich history that has evolved over time, shaping the way we classify and identify living organisms.
The concept of Binomial Nomenclature was pioneered by Carl Linnaeus, a Swedish botanist, who introduced the system of naming species with a two-part name in the 18th century.
In today’s scientific community, Binomial Nomenclature plays a crucial role in accurate identification and classification of species.